In 2014, the World Bank created the City Creditworthiness Initiative (CCI), co-funded by the Public-Private Infrastructure Advisory Facility (PPIAF), the Korean Green Growth Partnership, and the Rockefeller Foundation. Working in developing countries, CCI aims to bolster cities’ access to finance for infrastructure investment by working to develop creditworthy financial practices and supportive institutional, legal & regulatory enabling environments.
CCI engages via three primary methodologies: creditworthiness academies, creditworthiness technical assistance programs and creditworthiness knowledge and research products.
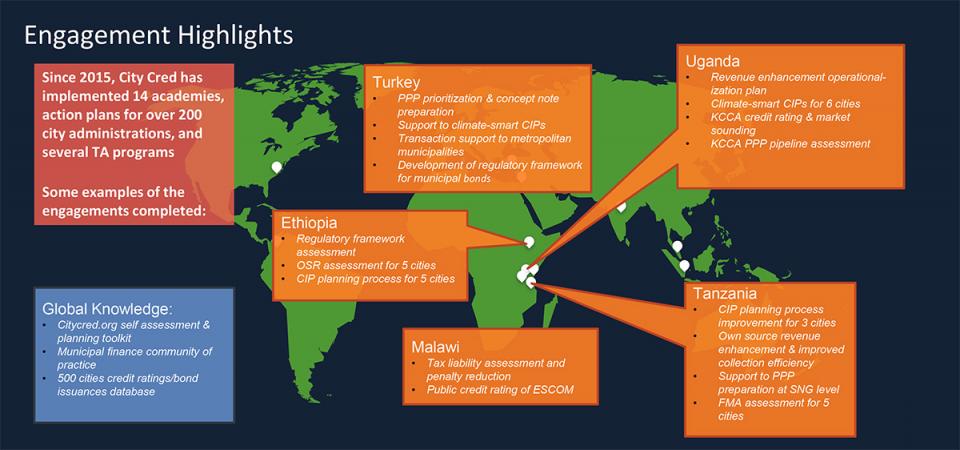
The academies are learning platforms that teach city leaders core principles of creditworthiness, including revenue management, expenditure control and asset maintenance, capital investment planning, and debt management. The academies also use a self-assessment toolkit (see below) in order to create a preliminary creditworthiness action plan. The technical assistance programs on the other hand are multi-year, customized "hands on" packages that help cities reach specific milestones in building best-practice financial management.
In addition to direct engagement with cities, CCI also seeks to address the knowledge gap that exists in the area of sub-national borrowing, in particular in terms of understanding the legal & regulatory environments and types/levels of borrowing engaged in by local governments in developing countries through its Local Government Borrowing Database.
CCI is a program within the World Bank’s Urban, Disaster Risk Management, Resilience & Land Group (GPURL).

Academies are intensive 3-5 day workshops with City authorities covering context specific factors affecting performance. These events typically occur on site in-country, and local government officials of selected cities are invited to attend. Prior to an academy, the CCI team conducts up-front analytics and direct engagement with cities & other stakeholders to identify core issues, which then frame the agenda. Legal & regulatory activities can be included in academies or have a separate process as needed.
Self Assessment – City Cred Tool
CCI offers a free self-assessment tool for city administrators to analyze their fiscal and regulatory conditions inhibiting creditworthiness. Our program uses the tool during Academies: participants work through the tool to develop a customized draft City Creditworthiness Improvement Action Plan (CCIAP) of specific institutional reforms, capacity building, and other actions aimed at improving their creditworthiness and facilitating their ability to plan, finance and deliver infrastructure services.
Improvement Action Plans (CCIAPs)
Working with development partners, CCI provides in-depth, multi-year, customized technical assistance programs to help cities achieve important steps on the pathway to creditworthiness and access to finance. The range of interventions is wide, encompassing everything from improving national legal and regulatory frameworks, to improving revenue collection and management systems, and reforming capital improvement planning and budgeting.
 CCI leverages insights gained from academies to bring short-, medium- and long-duration technical assistance and training activities to client cities. These are designed to help local governments achieve critical milestones on the pathway to creditworthiness and access to finance. This phase of the process will likely require one to four years, depending on each city’s creditworthiness status at the beginning of the process.
CCI leverages insights gained from academies to bring short-, medium- and long-duration technical assistance and training activities to client cities. These are designed to help local governments achieve critical milestones on the pathway to creditworthiness and access to finance. This phase of the process will likely require one to four years, depending on each city’s creditworthiness status at the beginning of the process.

The City Creditworthiness Initiative - Local Government Borrowing Database (CCI-LGBD) is a pilot research product comprised of quantitative and qualitative information that describes the enabling environment and experience of local governments in respect to debt. The CCI-LGBD is a joint World Bank-IFC activity. The objective of the database is to add to the global knowledge of local government borrowing in developing countries and specifically in IBRD/IDA recipient countries. The methodology consists of internal and external desk research. Internal desk research involves existing World Bank data and resources. External desk research involves mainly government reported data from official in-country statistical bureaus (i.e. departments of treasury, offices of audit and other official sources). In this sense the CCI-LGBD is not World Bank data: it is a collation of statistical information from official in-country sources. The World Bank makes no representations on the data beyond its status as product of official sources by national and/or local governments. This is a core difference from other World Bank products in this space – notably World Bank International Debt Statistics – in which the data is survey-based and a direct product of the World Bank.
Because of its value in supplementing scarce sub-national statistics, the CCI-LGBD is released as a public good. Ultimately the research will cover between 30-40 countries, to be updated on an as-needed basis.